The Role of PCSK9 in the Pathophysiology of Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is pathologically characterized by the subendothelial buildup of lipids, extracellular matrix, and cholesterol-laden macrophages, which collectively form atherosclerotic plaques. The liver-secreted protein PCSK9 promotes the lysosomal degradation of the hepatic LDL receptor (LDLR) through direct binding. This process impairs LDL clearance and elevates circulating LDL-C (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol), a central driver in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Consequently, this pathophysiological pathway establishes PCSK9 as a validated therapeutic target for treating atherosclerosis.
From Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs) to siRNA Therapeutics
Several anti-atherosclerotic therapies targeting PCSK9 have been developed, primarily including mAbs such as Alirocumab and Evolocumab, and more recently, siRNA-based agents like Inclisiran— all aimed at lowering LDL cholesterol and reducing cardiovascular risk.
While mAbs function by binding and neutralizing circulating PCSK9 protein, siRNA therapies act within hepatocytes to degrade PCSK9 messenger RNA (mRNA). This results in a more pronounced and durable suppression of the body’s own PCSK9 production. The transition to siRNA platforms is further supported by clinical advantages: agents such as inclisiran require less frequent dosing (e.g., twice yearly) compared to the monthly or bi-weekly injections needed for most mAbs, thereby improving patient adherence and potential long-term outcomes.
A New Tool to Model ASCVD: AAV-PCSK9
To evaluate the efficacy of potential therapeutics, GemPharmatech has established an atherosclerotic mouse model using AAV-mediated delivery of a mutant human PCSK9 (hPCSK9) gene. This model enables direct in vivo assessment of PCSK9-targeted compounds and yields findings with high translational relevance to human biology.
AAV-hPCSK9 delivery, combined with a Western diet, induced increase in plasma hPCSK9 level, hyperlipidemia and atherosclerotic plaques.
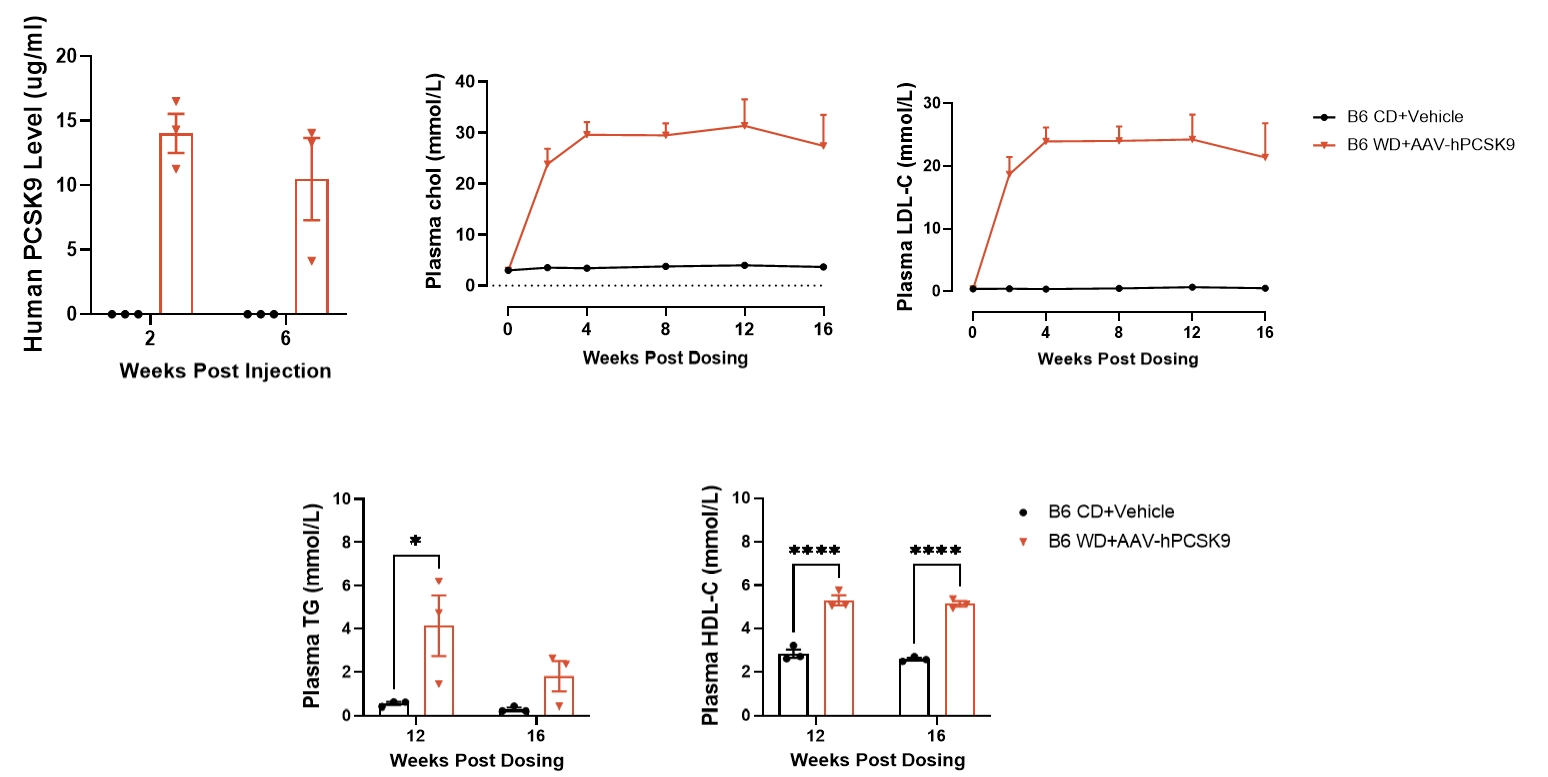
Figure 1. AAV-hPCSK9 + WD induced hyperlipidemia
Sustained expression of hPCSK9 in mice can be achieved following AAV-hPCSK9 injection. When combined with a Western diet for 4 weeks, this intervention induces a robust hyperlipidemic phenotype in mice, which is characterized by elevated levels of total cholesterol (CHOL), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C). Data are presented as Mean±SEM; n=3.
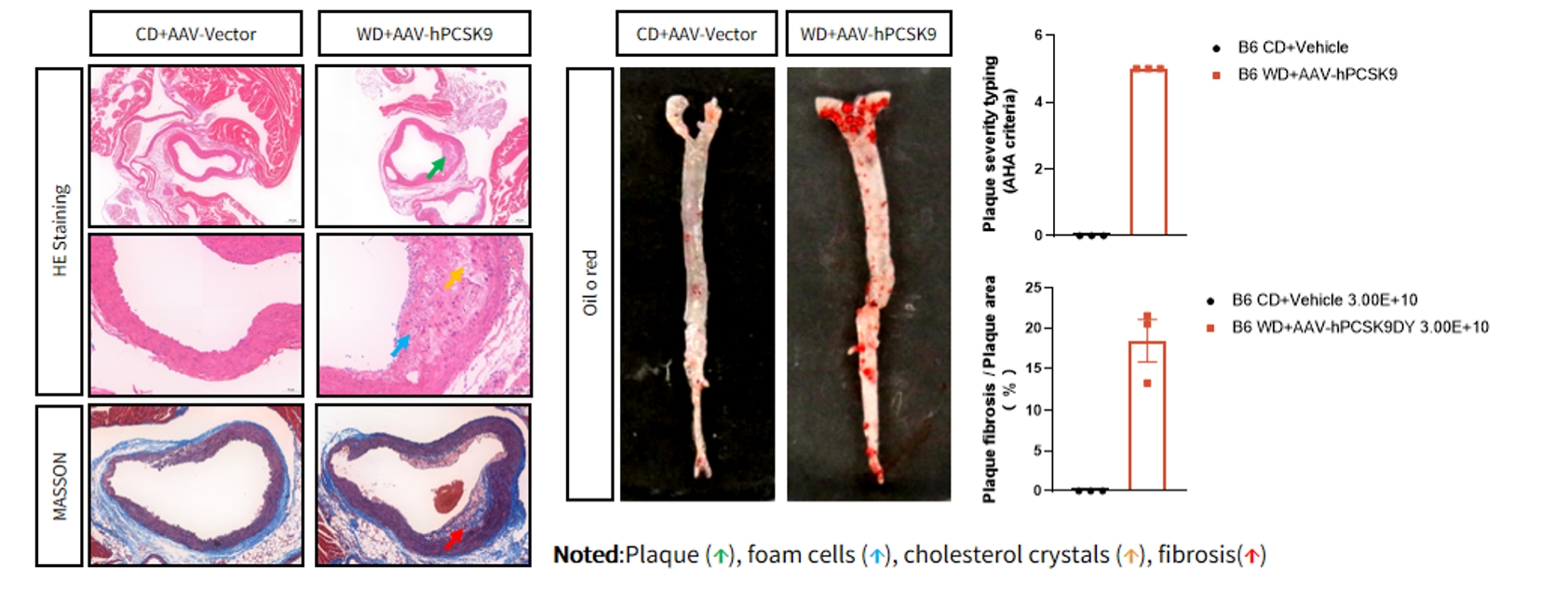
Figure 2. AAV-hPCSK9 + WD induced atherosclerosis
Multi-modality analysis comparing atherosclerotic lesion severity between control and WD+ AAV-hPCSK9 mice. The left panel displays representative histological sections, and the right panel presents en face aortic lipid staining and quantitative morphometric analyses. Data are presented as Mean±SEM; n=3.
Aortic root atherosclerotic plaque severity typing (AHA criteria): type I, initial lesion: few foam cells; type II, lipid streak: with multiple layers of foam cells; type III, preatherosclerotic with extracellular lipid pools; type IV, atherosclerotic, with fused extracellular lipid pools; type V, fibrous plaque with a lipid core; type VI, complex plaque with surface defects, hemorrhages, or thrombi Complex plaques; type VII, plaques with calcification.
Providing the Very Latest in Mouse Models and Preclinical Services
Whether you are testing the efficacy of a new drug that requires a model that faithfully recapitulates a disease or just need a knockout targeting a specific gene, GemPharmatech is the trusted partner for genetically engineered models and preclinical services. With model creation expertise, experience with numerous diseases, and proven reliability generating trustworthy data, we provide the insights that help scientists accelerate their research and drug discovery.
Are you ready to explore how GemPharmatech can help you accelerate your own success?
Contact GemPharmatech today and let's start a conversation.